News
ALPhANOV's historical know-how in laser processing
 Laser processing, and more specifically surface engineering, is at the core of ALPhANOV's identity. It is through laser processing that we were able to demonstrate the incredible potential of photonics technology for industrial applications.
Laser processing, and more specifically surface engineering, is at the core of ALPhANOV's identity. It is through laser processing that we were able to demonstrate the incredible potential of photonics technology for industrial applications.
Year after year, our team members have pushed the limits of what photonics can do. We have developed new laser processing for machining new materials, with ever more complex shapes and challenging scales.
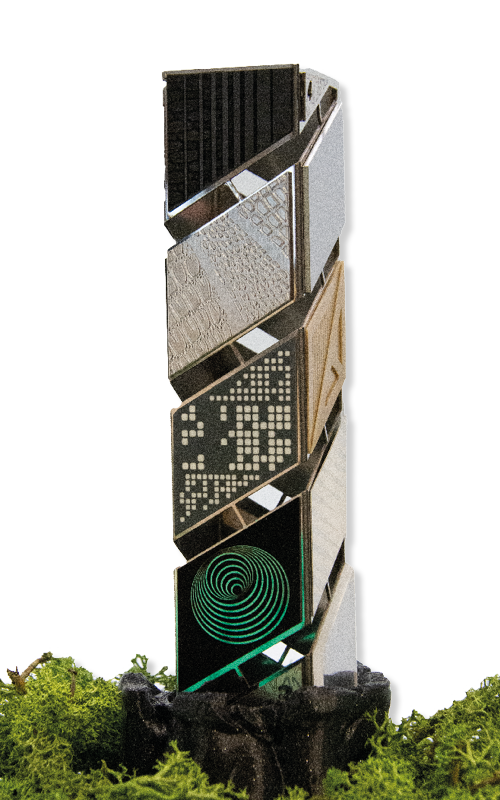
This demonstration piece is the legacy of this unique know-how. Each side of this tower is made up of samples of materials and lacer processing that we are able to produce, and which have enabled spectacular advances in terms of productivity, quality of finish and, more broadly, have transformed many industries.
Much more than 16 facets
Our expertise in surface engineering has grown considerably over the past 17 years, and the multi-disciplinary nature of our team members means we can adapt to any situation. We are able to machine any material using multiple laser processing, on scales ranging from nanometers to meters.
We have linked together all the processing used in the manufacture of this part.
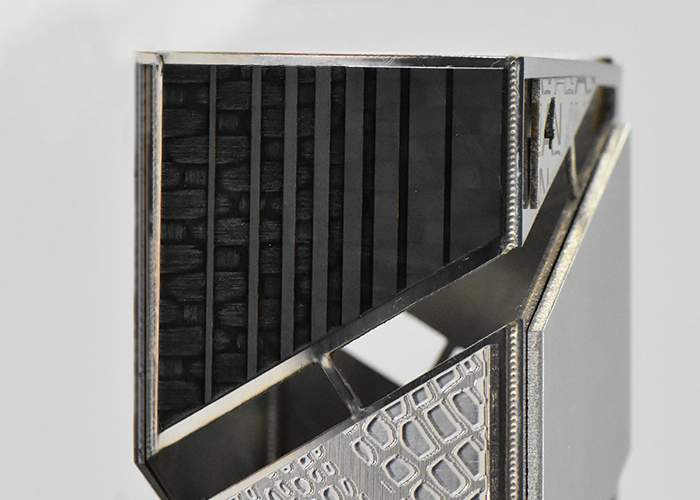 |
CFRP (carbon fiber reinforced polymer): Selective ablation The selective ablation process allows removal of the CFRP polymer matrix without damaging the fibers, which is essential for structural bonding applications in aerospace, aeronautical and automotive industries.
|
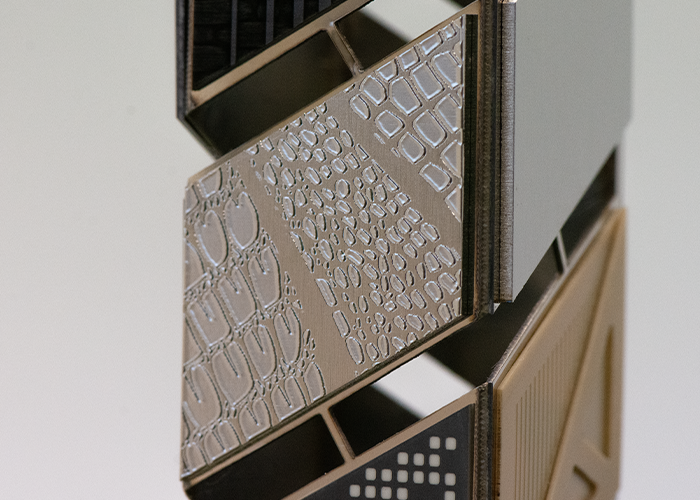 |
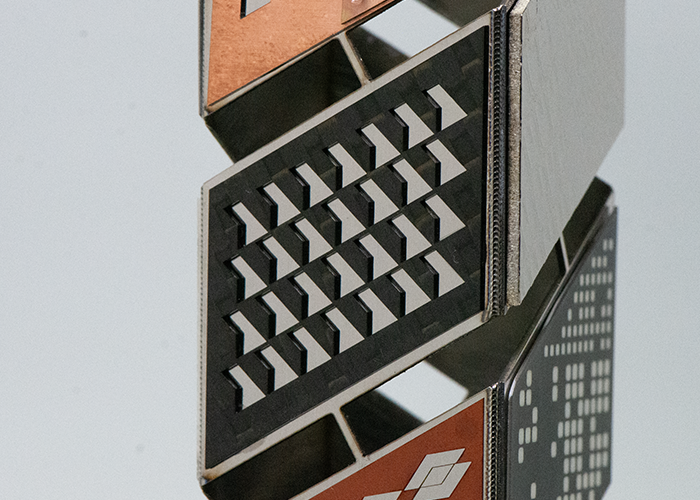
Titanium (metal): Reshaping Titanium reshaping enables us to rapidly obtain high aspect ratio surface morphologies, used for aesthetic or functional applications, such as the shaping of injection molds. |
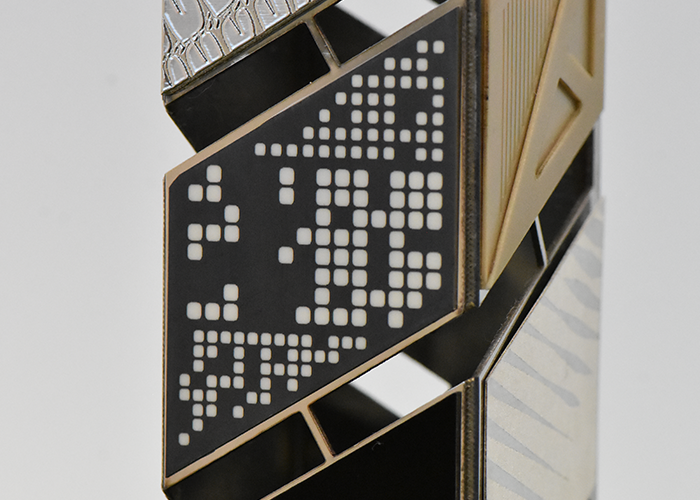 |
Zirconia (ceramic): Coloration Zirconia surface coloring is used for aesthetic rendering or marking, facilitating traceability. |
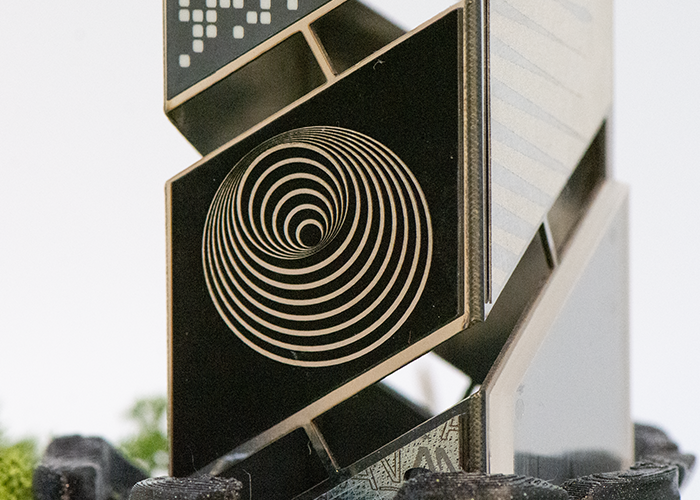 |
Stainless steel (metal): Blackening Blackening of stainless-steel increases light absorption in the visible spectrum and emissivity in the infrared spectrum, creating a light-trapping effect. |
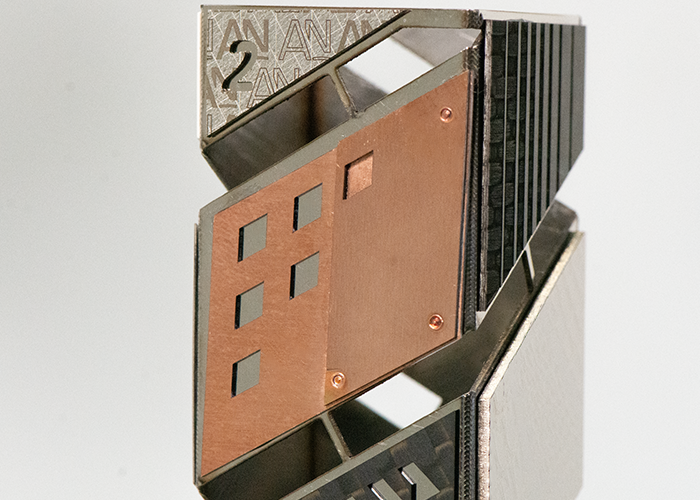 |
Copper (metal): Cutting and welding Copper cutting and welding are commonly used to work on electrodes or PCBs in the electromobility and microelectronics fields. |
 |
CFRP (carbon fiber reinforced polymer): Cutting Cutting CFRP is essential for working with composite materials in the aerospace field, enabling assembly without thermal alteration of the polymer matrix and without delamination of the composite. |
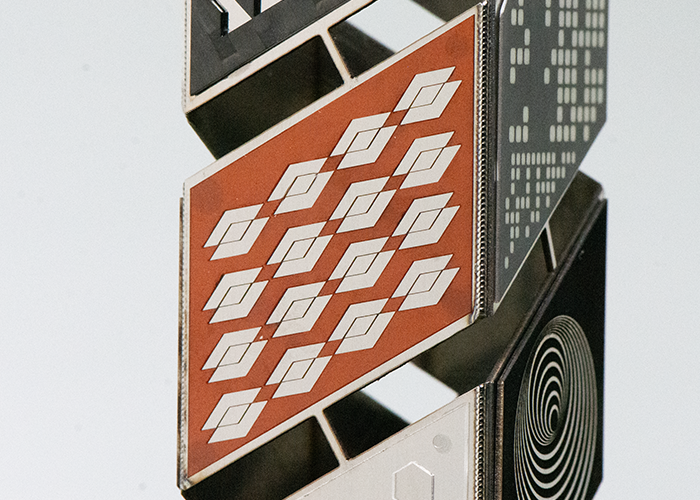 |
Kapton (polymer): Cutting Cutting kapton with femtosecond lasers is used in medical, electronics and aerospace applications, offering optimum edge qualities and enabling very low thicknesses to be cut without film deformation (<10 µm). |
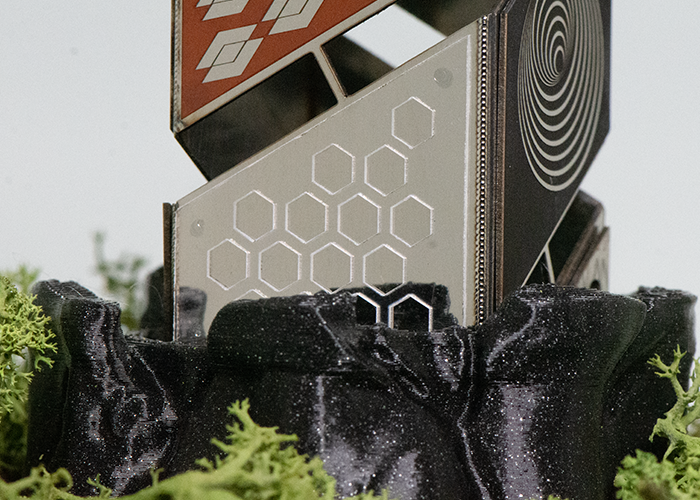 |
Glass: Cutting Cutting glass from bottom up top with a low taper is used in microelectronics, defense, display and photovoltaic applications. |
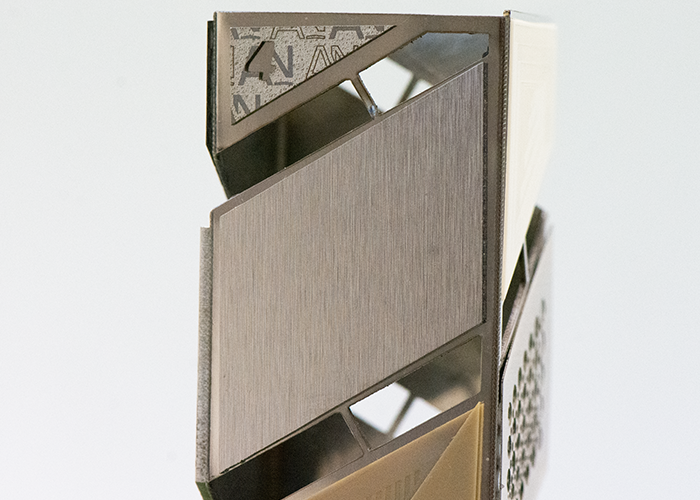 |
Titanium: Texturing Titanium texturing is used for aerospace applications, where reshaping is often applied to molds for mechanical parts. |
 |
Peek: Welding and texturing Peek welding and texturing have many applications in the medical, electronics and aerospace fields. |
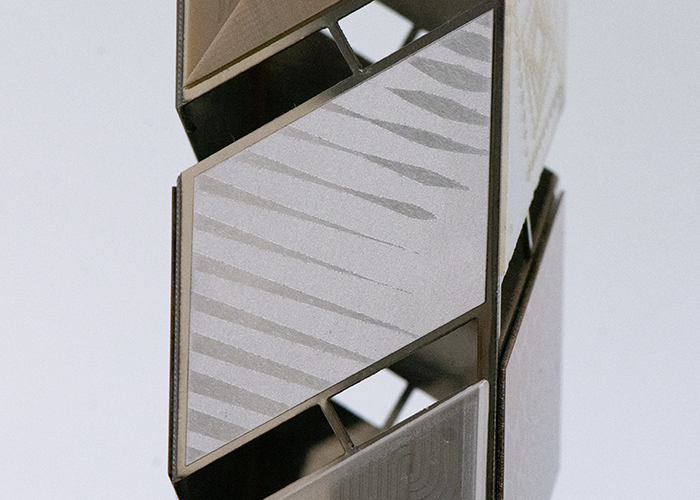 |
Aluminum: Bleaching Aluminum bleaching increases reflectivity in the visible spectrum, with applications in aerospace, marking and aesthetics. |
 |
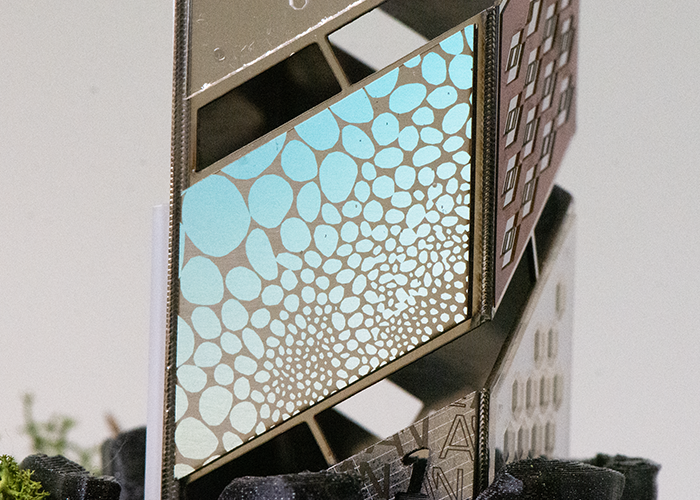
Sapphire: Intra-volume grating inscription Intra-volume grating in sapphire creates diffractive effects that modify the refractive index, used for anti-counterfeiting markings and decorative applications. Sapphire cutting is also used in watchmaking. |
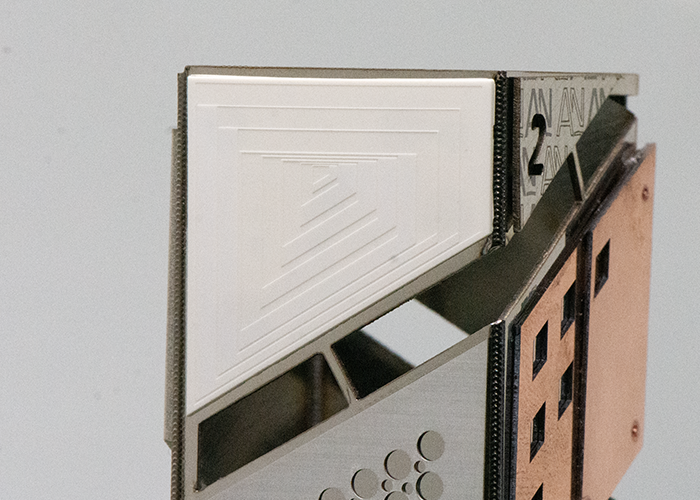 |
Alumina: Ablation Controlled ablation of alumina is used in biomedical applications, such as dental implants, and in microelectronics applications. |
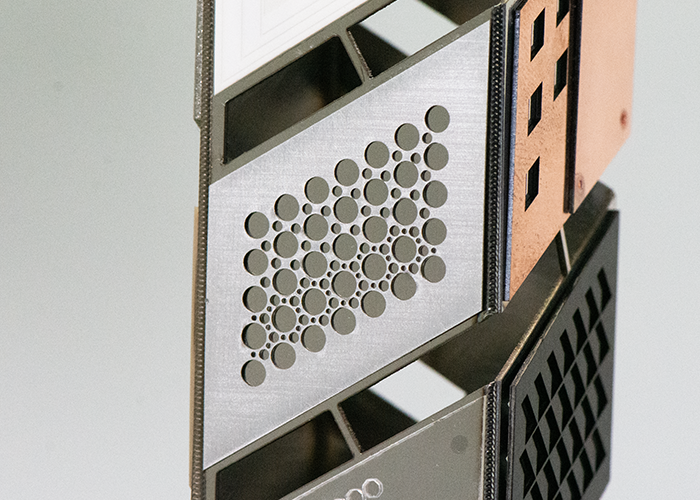 |
Aluminum: Cutting Aluminum cutting enables fast, small-diameter assembly or drilling. |
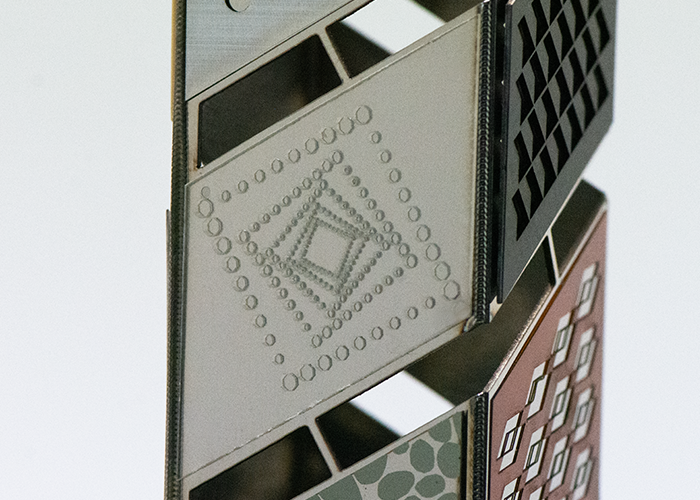 |
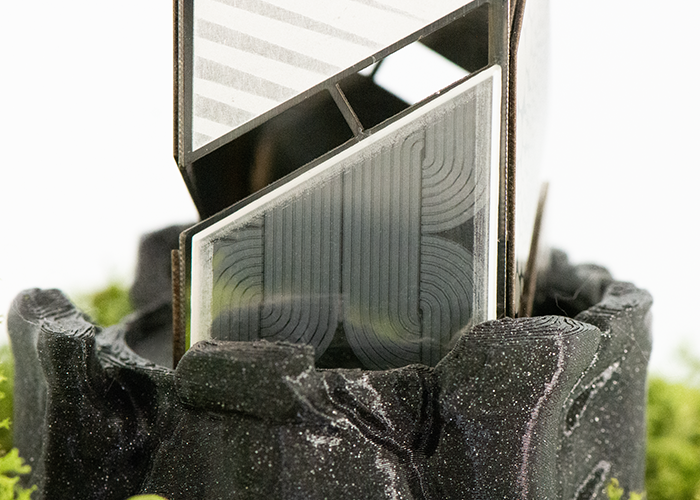
Glass: Drilling Glass drilling with an aspect ratio of 5, without thermal effects, is used in a variety of applications. |
 |
Stainless steel: LIPSS Surface functionalization of stainless steel by LIPSS creates hydrophilic or hydrophobic surfaces, with antibacterial applications. |
We're proud to be able to present such an achievement.